Welcome to eaQTLdb
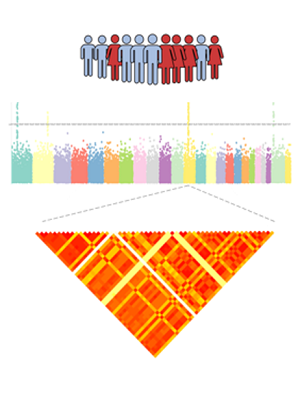
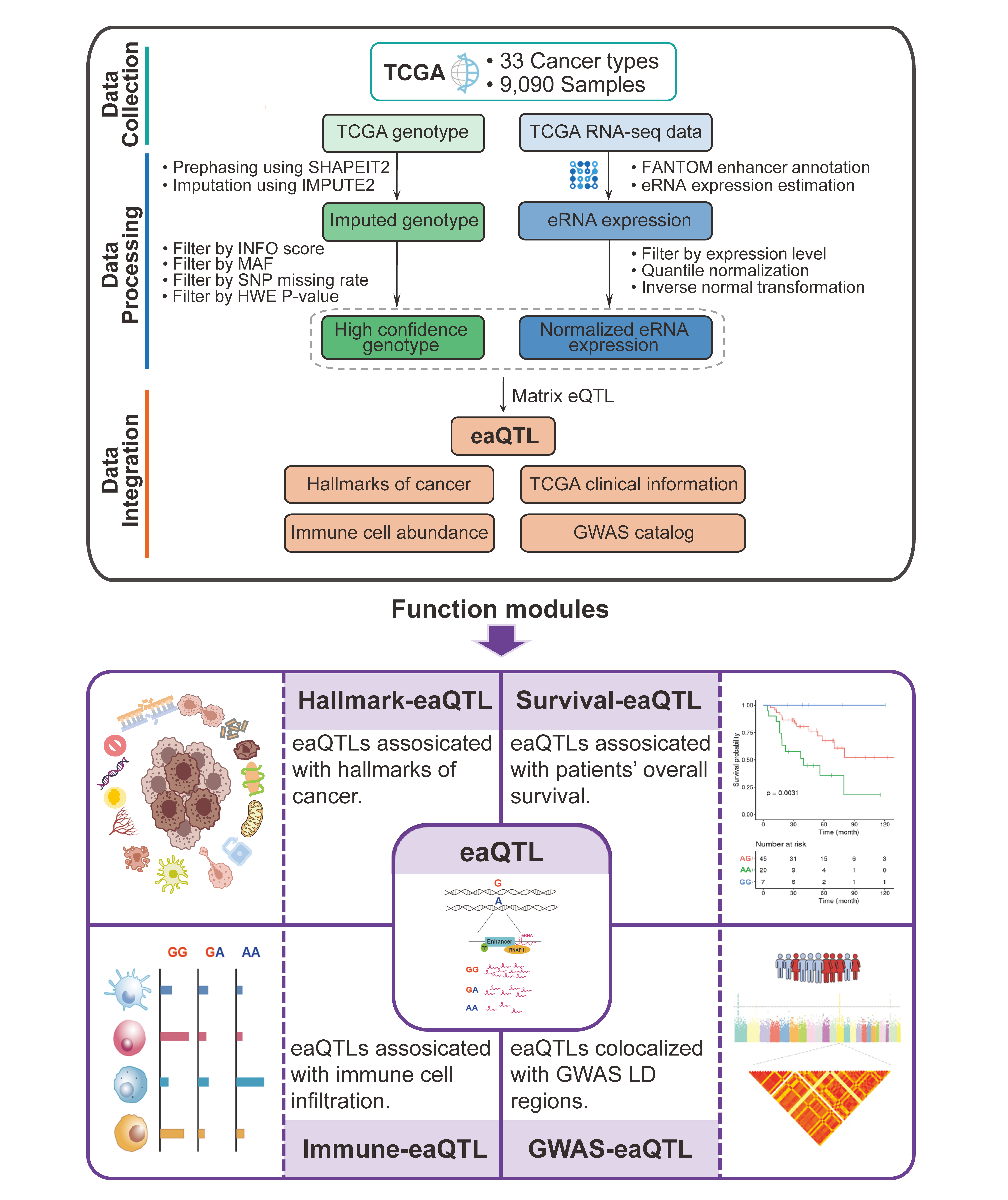
Enhancers are distal regulatory DNA elements that are critical for regulation of gene expression program. Besides the key roles in determining cell identity by establishing cell-type-specific expression patterns, enhancers have been increasingly recognized as important players in the pathogenesis of human complex diseases, such as cancer. Emerging studies have revealed that active enhancers could be pervasively transcribed into noncoding RNAs called enhancer RNAs (eRNAs), which could be used as an index of enhancer activity. Aberrant expression level of eRNAs is highly associated with enhancer malfunction and have been demonstrated in multiple cancer types. Despite indispensable roles of eRNA in gene regulation, the contributions of genetic variation to eRNA expression remain largely unexplored. The eaQTLdb is a comprehensive database for exploring enhancer activity quantitative trait loci (eaQTL) which are referred as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that affect eRNA expression based on multi-omics data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA).
What can eaQTLdb do
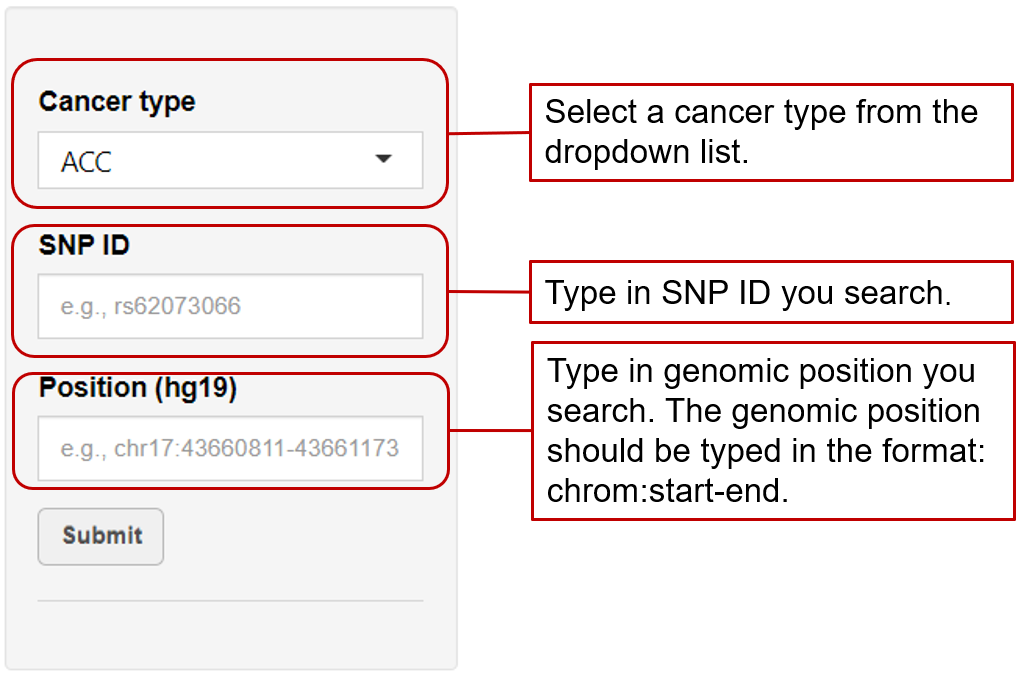
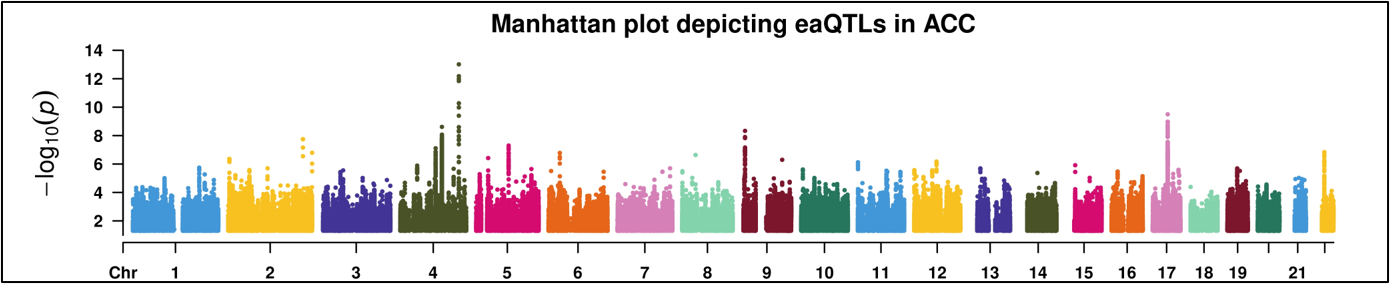
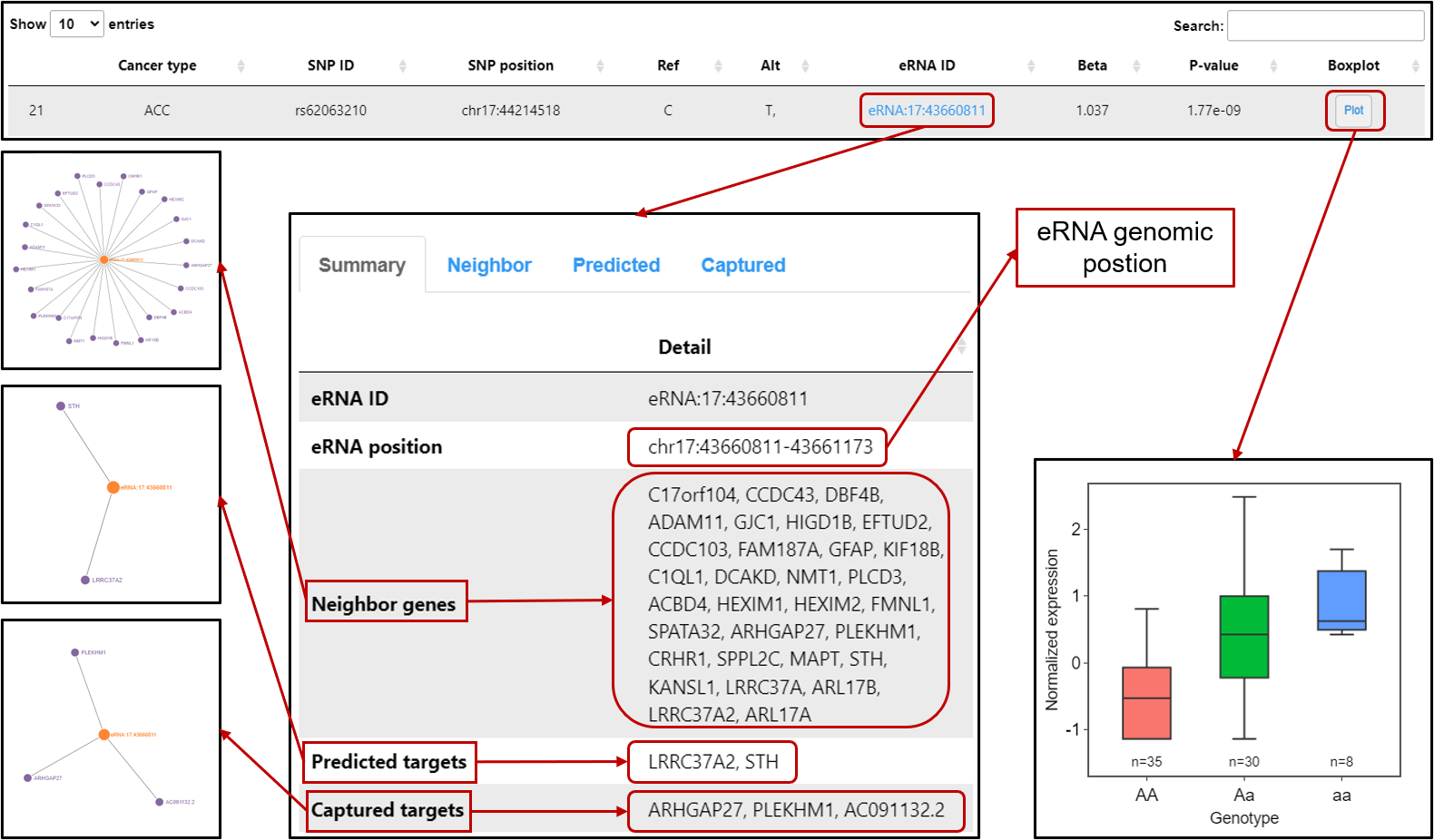
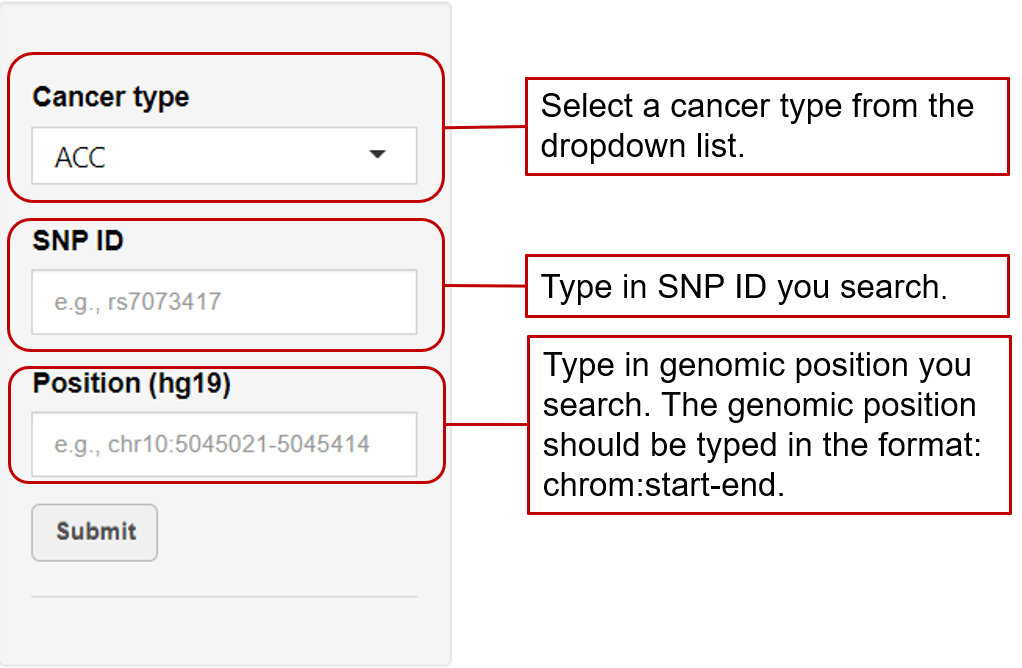
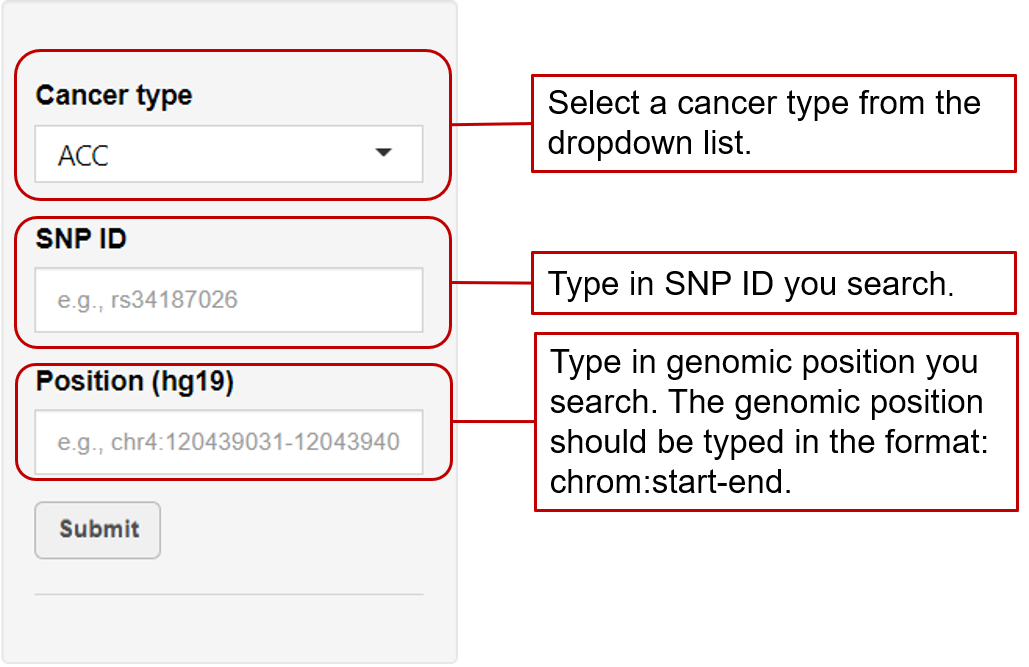
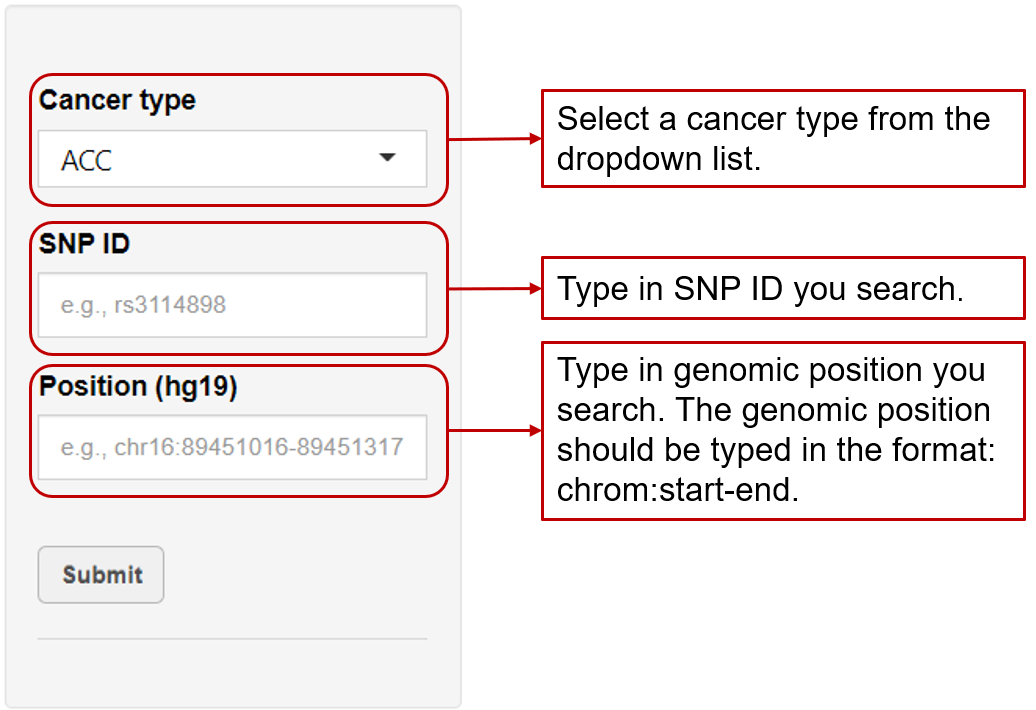
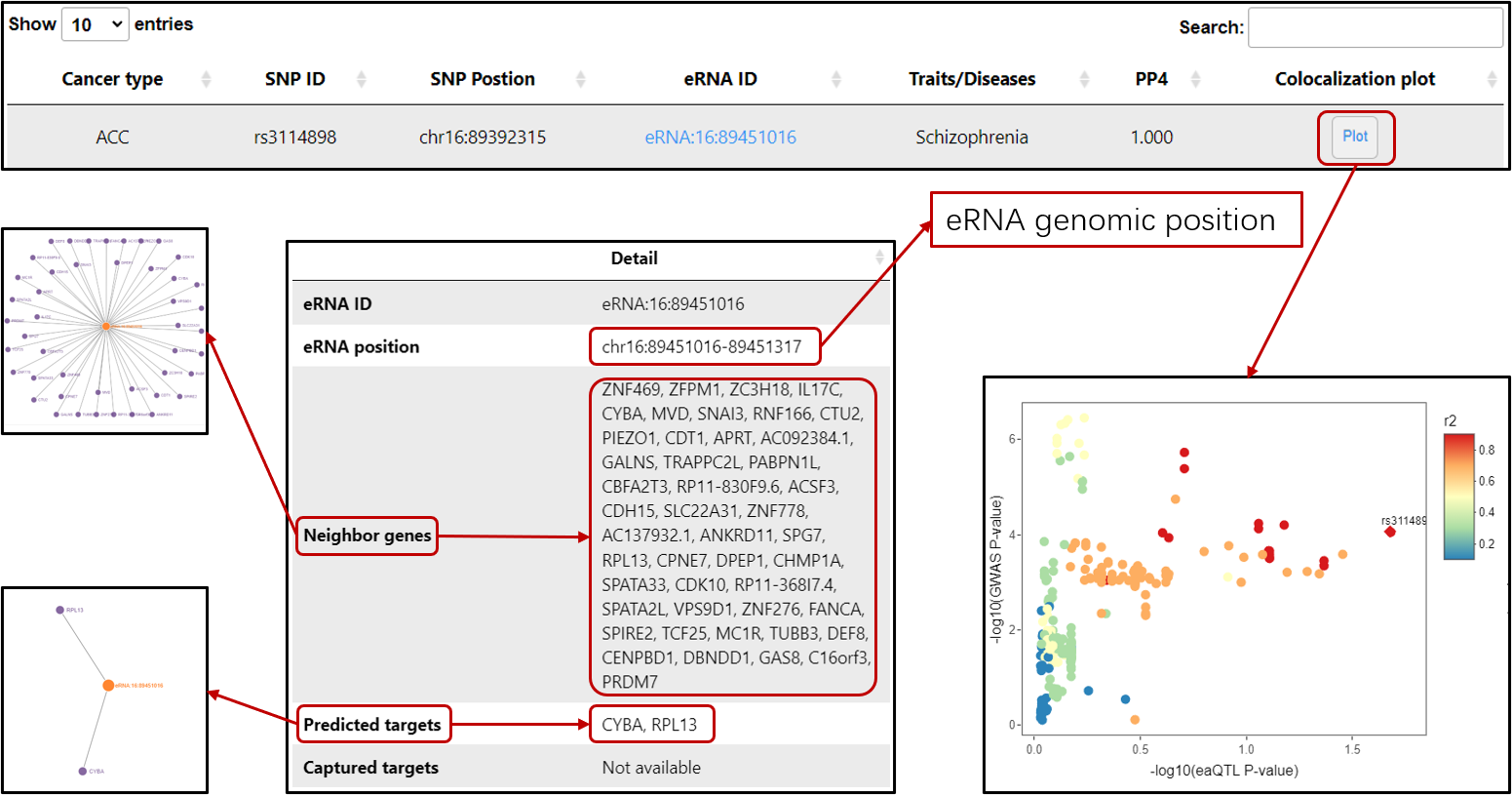
eaQTL: Browse or search eaQTLs across different cancer types
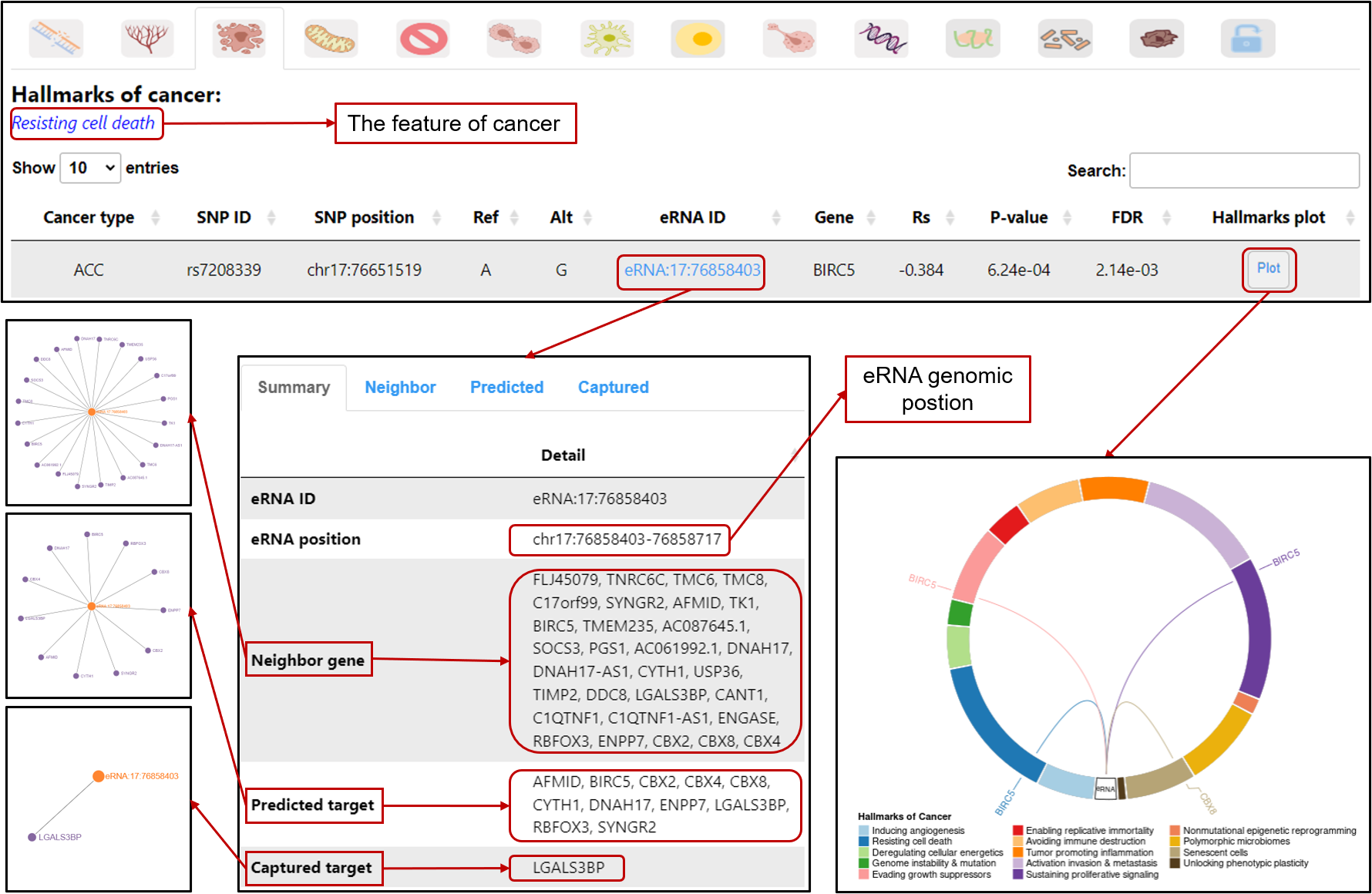
Hallmark-eaQTL: Browse or search eaQTLs associated with hallmarks of cancer
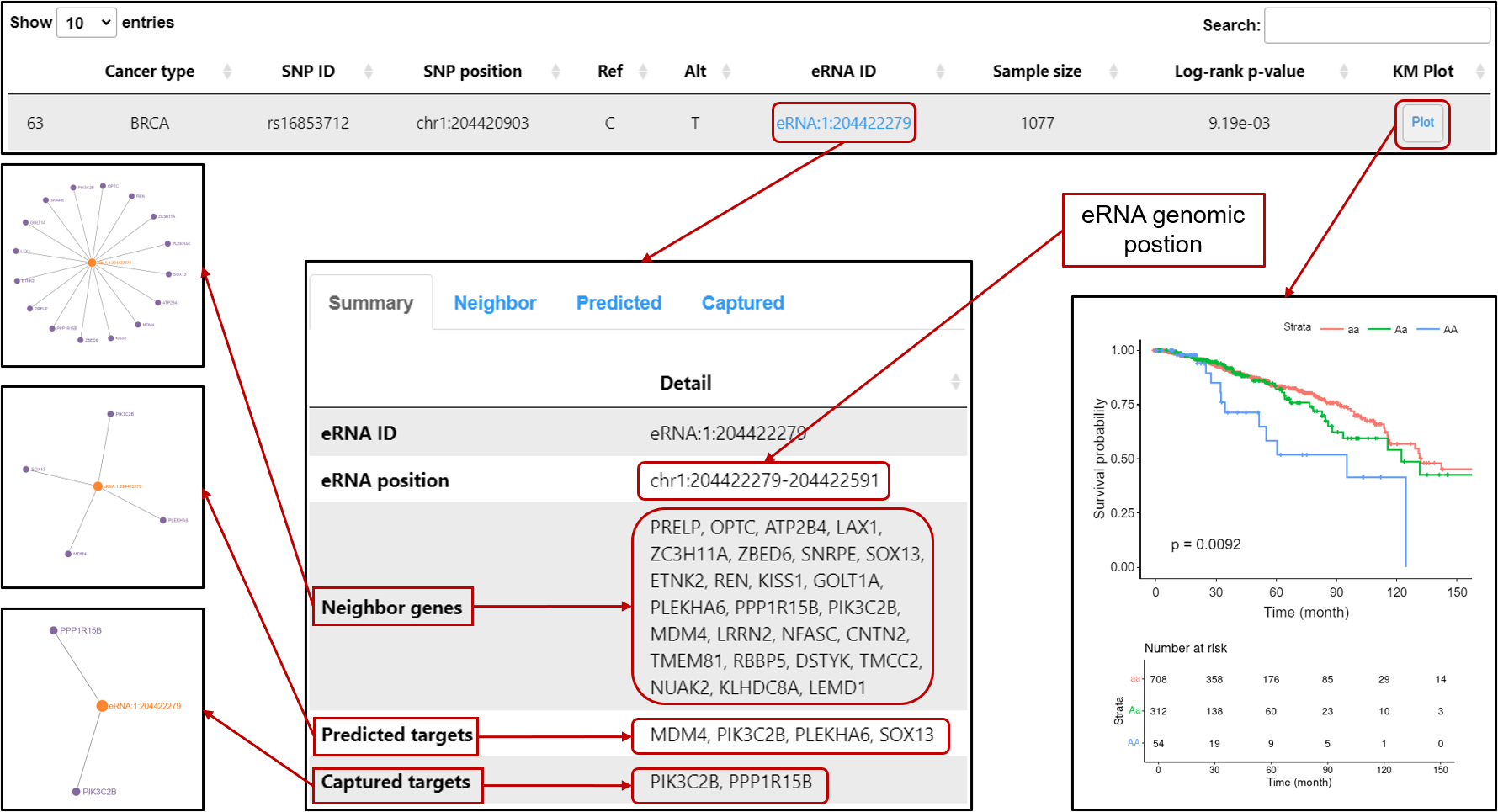
Survival-eaQTL: Browse or search eaQTLs associated with patients' overall survival
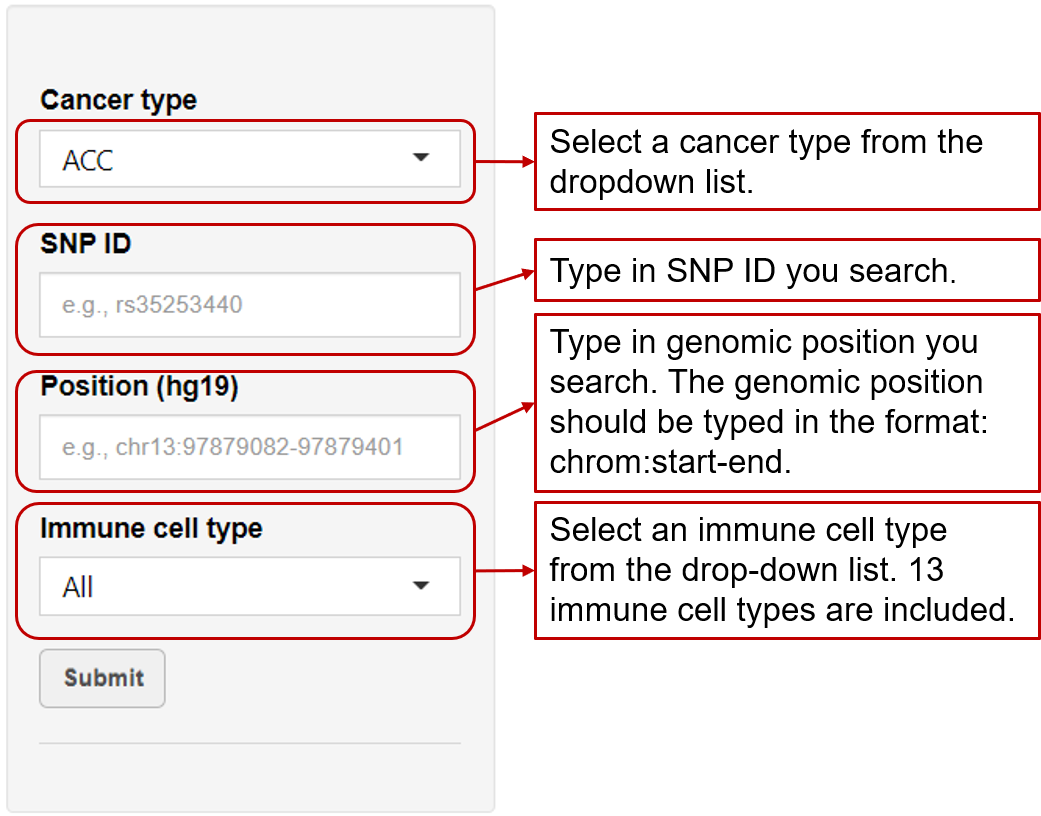
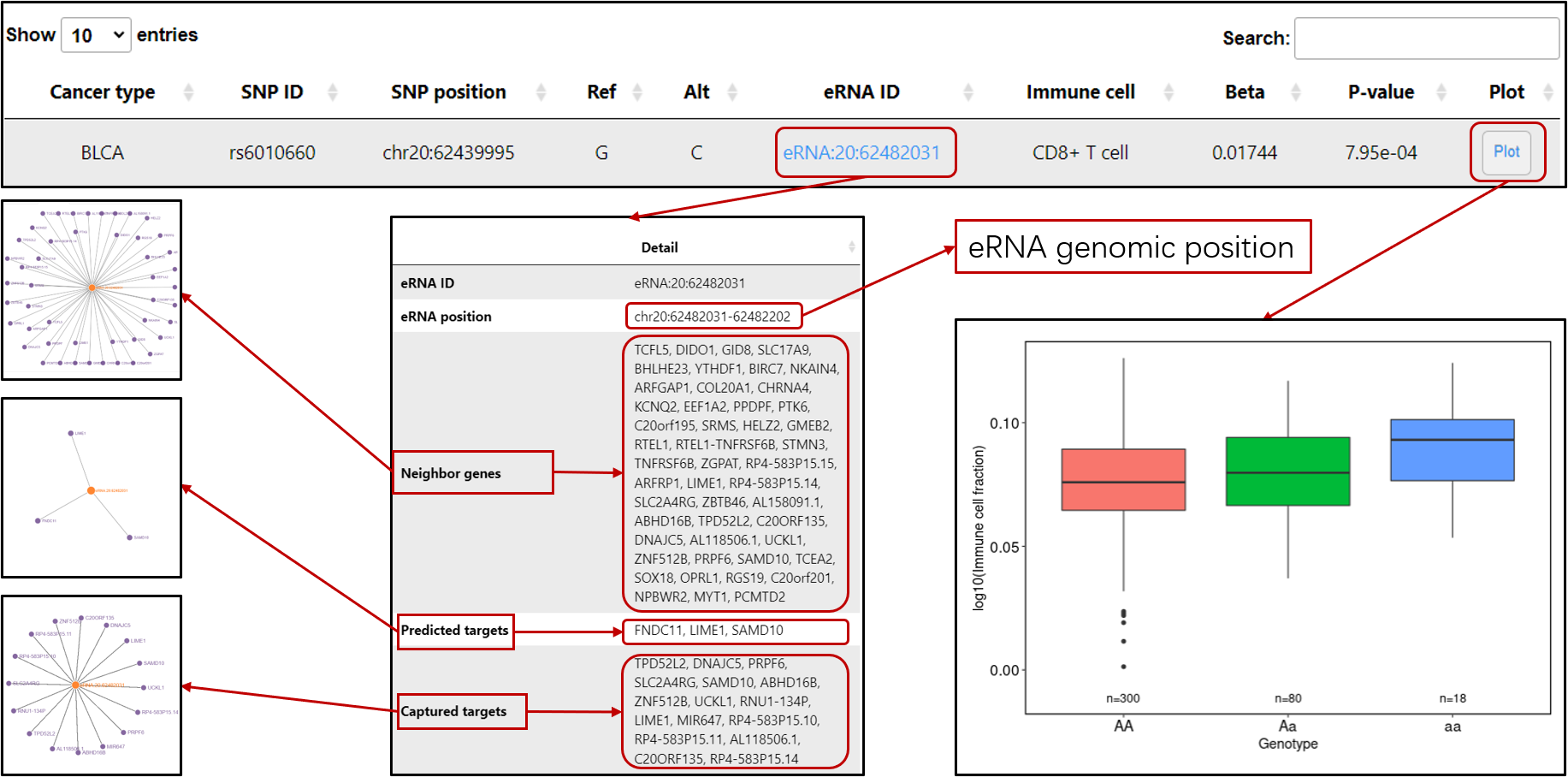
Immune-eaQTL: Browse or search eaQTLs correlated with immune cell infiltration in tumors
GWAS-eaQTL: Browse or search eaQTLs colocalized with diseases/traits-associated SNPs
Download: Download all browsed or searched eaQTL results
How to cite
eaQTLdb: An atlas of enhancer activity quantitative trait loci across 33 cancer types
Jiapei Yuan, Yang Tong, Xiaochuan Liu, Mulin Jun Li, Qiang Zhang, Yang Yang (2023) Int J Cancer
Function Modules
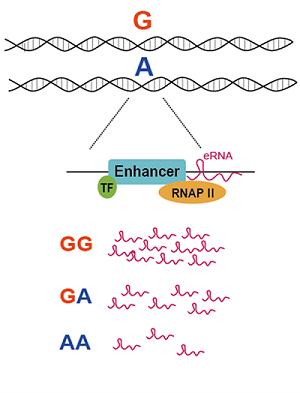
eaQTL
Hallmark
Survival
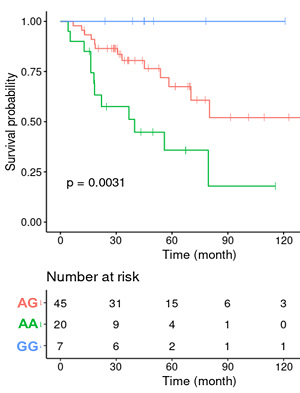
Immune
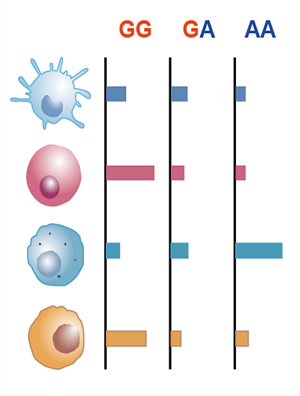
GWAS